- Statistics
- Challenges
- Housing
- Brooding of Chicks
- Caring of chicks
- Diseases & Parasite Control
- Vaccination
- Important nutrients in feeding
Some Important Statistics
| Country | Human population | Chicken population | Chicken per person |
| Kenya | 57,296,715 | 58,735,648 | 1.0 |
| Uganda | 50,043,944 | 76,000,000 | 1.5 |
| Tanzania | 64,801,445 | 72,000,000 | 1.1 |
| Kenya is importing chicken products from other countries-Europe, Egypt, Uganda, Turkey, Saudi Arabia S. Africa | |||
Issues? Challenges Facing Chicken Production
ISSUE | SOLUTION |
Low genetic potential | Leverage on Improved Kienyeji |
low productivity-low volumes | Increase production levels (350) |
High cost of feeds | Of-farm production & formulation |
Diseases and parasites menace | Training of Village Business Advisors (VBAs/ToTs |
Low management skills-poor housing, poor feeding, etc | Continuous training and mentorship |
Poor marketing arrangements/not organized | Contractual chicken rearing |
Low extension services | Leverage on Trained ToTs |
Predators | Invest in strong Infrastructure (houses. Fence) |
Climate change- increased temperatures, low feeds production | Adoption of Climate smart technologies-Solar, Biogas, DTCs etc |
Housing of chicken
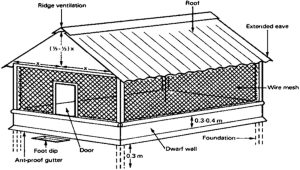
Simple Housing
Well ventilated, protection from predators, Run for birds to get sun-light, Accessible area, Strong Local materials, Clean, Space-1sq Ft per bird

- You can have a separate room for brooding the chicks up to 1 month. You can also use the main chicken room and provider chick brooder.
- Chick brooder should have all necessary equipments-brooding jiko, chick feeders, chick drinkers and round shaped fly wood; See photo of chick brooder below.

- Keep birds confined, remembering, however, that rodents, snakes, and other predators can dig under walls.
- Securely covering windows with heavy-gauge mesh wire or screening helps keep out predators as well as wild birds, which can be sources of disease.
- It is important to bury the wire along the fence border at least 12 inches deep and to toe the fence outward about 6 inches. Taking these precautions will stop predators from digging under the fence.
- To prevent problems with hawks and owls, cover your outside runs with mesh wire or netting. (See house photo two above)
- To protect your flock from theft, lock the building and pens securely whenever you are not at home.
- Also, keeping a protective dog near your unit usually works well to discourage predators and unwanted visitors.

- Much of the poultry diseases start at hatchery and breeder stock level due to poor houses.
- As a routine one day old chicks are supposed to be treated with a lot of care otherwise diseases can be passed on to the entire flock.
- Ensure your poultry house is built in a manner to prevent infections and parasites. There should be a room “ward” where sick birds are kept and treated accordingly after being isolated from the flock.
Control of Parasites
- External parasites; -These includes; –
- Poultry louse, fleas, -Controlled by use of Servin dudu dust
- Mites-Controlled by use of Oil (fresh 2T oil, salad oil, Vaseline jelly –by rubbing on the legs to suffocate the mites
- Soft ticks– Controlled by use of either ‘Vectorclor, Actellic Liquid’ –by thoroughly spraying the house weekly for four weeks
- Internal parasites include: –
- Worms-Controlled by use of Ascarex, Piperazine, and other commercial dewormers-deworming is done every two months
- Coccidia-Prevented by use of coccidiostats in the commercial feeds and treated by use of Amprolium, coccid and other drugs in the market

Poultry farmers must keep surveillance of the following diseases and ensure their birds are vaccinated against them at the recommended time.
- Newcastle disease (NCD)
- Infectious Bronchitis (IB)
- Infectious Bursal disease (IBD) also called Gumboro
- Fowl typhoid (green secretion)
- Fowl pox
- Fowl cholera (Watery diarrhoea)
Vaccination Regime
(Age) | Vaccine nature | Route |
Day 1 (after hatching) | MAREKS | At the hatchery |
Before day 10 | NCD + IB | Eye drop/Nasal/Mouth |
Week 3 | IBD (GUMBORO) | Oral |
Week 12 | NCD + IB (booster dose) | Eye drop /Nasal/Mouth |
3-6th Week | FOWL POX | Wing stab |
8th Week | FOWL TYPHOID | Intra-muscular |
Every 3 months | NCD + IB | Eye drop/Nasal |
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins: Soybean meal, Canola, Cotton seed meal,Corn gluten meal, Sunflower seed meal, Fish, Prawns
- Fats: Animal and vegetable fats are the highest energy sources in feedstuffs
- Vitamins: A,D,E,K-Fat soluble, B and C-water soluble
- Minerals: Grains are low in minerals so supplements are necessary Sources: Bone meal, Egg shells, Di-calcium phosphate(DCP), Mono-calcium phosphate(MCP),Salt(NaCl) Mineral premix, Limestone(stock lime)
- Water-Digestion, Transport within the body, cooling, production- 70%-Body Wt, 65%-Egg
Estimated feed intake at different ages for indigenous chicken (For confined Birds)
AGE IN WEEKS | INTAKE /Bird/Day (Grams dry wt) |
1 | 13 g |
2 | 18 g |
3 | 28 g |
4-6 | 40 g |
7-8 | 55 g |
9-15 | 74 g |
16-27 | 90 g |
28 and Above | 130 g |
